Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the week"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the week text) |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Huang iScience2022 25-8.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
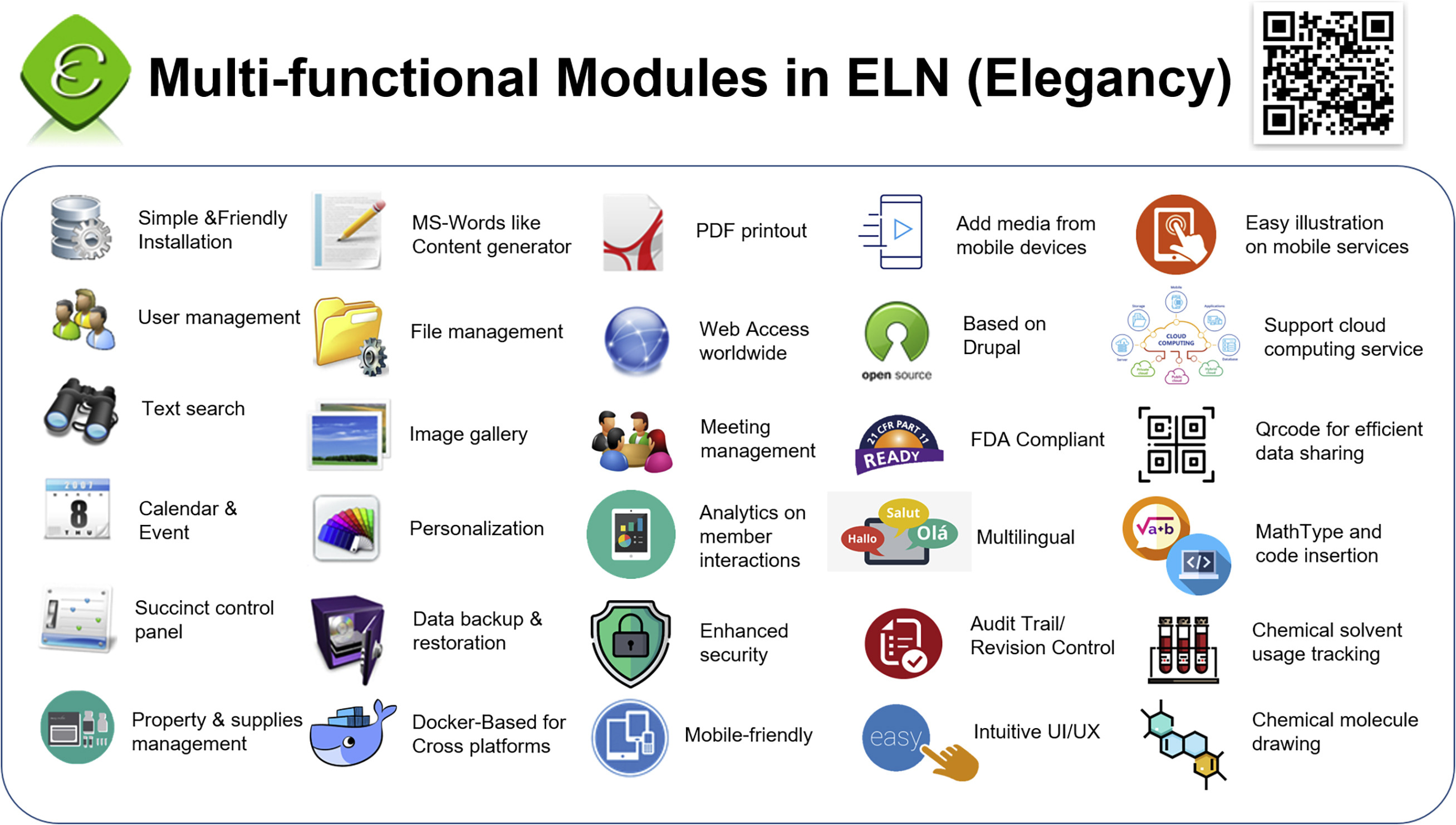
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Elegancy: Digitizing the wisdom from laboratories to the cloud with free no-code platform|Elegancy: Digitizing the wisdom from laboratories to the cloud with free no-code platform]]"''' | ||
[[ | One of the top priorities in any [[laboratory]] is [[Archival informatics|archiving]] experimental data in the most secure, efficient, and errorless way. It is especially important to those in chemical and biological research, for it is more likely to damage experiment records. In addition, the transmission of experiment results from paper to electronic devices is time-consuming and redundant. Therefore, we introduce an [[Open-source software|open-source]] no-code [[electronic laboratory notebook]] (ELN), Elegancy, a [[Cloud computing|cloud-based]]/standalone web service distributed as a Docker image. Elegancy fits all laboratories but is specially equipped with several features benefitting biochemical laboratories. It can be accessed via various web browsers, allowing researchers to upload photos or audio recordings directly from their mobile devices. Elegancy also contains a meeting arrangement module, audit/revision control, and laboratory supply management system. We believe Elegancy could help the scientific research community gather evidence, share information, reorganize knowledge, and digitize laboratory works with greater ease and security ... ('''[[Journal:Elegancy: Digitizing the wisdom from laboratories to the cloud with free no-code platform|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
{{flowlist | | {{flowlist | | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Implementing an institution-wide electronic laboratory notebook initiative|Implementing an institution-wide electronic laboratory notebook initiative]] | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:Quality and environmental management systems as business tools to enhance ESG performance: A cross-regional empirical study|Quality and environmental management systems as business tools to enhance ESG performance: A cross-regional empirical study]] | ||
* [[Journal: | * [[Journal:PIKAChU: A Python-based informatics kit for analyzing chemical units|PIKAChU: A Python-based informatics kit for analyzing chemical units]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:08, 10 April 2023
"Elegancy: Digitizing the wisdom from laboratories to the cloud with free no-code platform"
One of the top priorities in any laboratory is archiving experimental data in the most secure, efficient, and errorless way. It is especially important to those in chemical and biological research, for it is more likely to damage experiment records. In addition, the transmission of experiment results from paper to electronic devices is time-consuming and redundant. Therefore, we introduce an open-source no-code electronic laboratory notebook (ELN), Elegancy, a cloud-based/standalone web service distributed as a Docker image. Elegancy fits all laboratories but is specially equipped with several features benefitting biochemical laboratories. It can be accessed via various web browsers, allowing researchers to upload photos or audio recordings directly from their mobile devices. Elegancy also contains a meeting arrangement module, audit/revision control, and laboratory supply management system. We believe Elegancy could help the scientific research community gather evidence, share information, reorganize knowledge, and digitize laboratory works with greater ease and security ... (Full article...)
Recently featured: